Relational Database Overview
Notes:
**The Relational Model **: - The central data description construct in this model is a relation, which can be thought of as a set of records, relation = Records - A description of data in terms of a data model is called a schema. Every relation has a schema. Ex, Students(sid: string, name:string) - integrity constraints: conditions that the records in a relation must. satisfy - Each relation has a collection of tuples(rows) - the schema for a relation specifies its name, the name of each field(or attribute or column)
DBMS: - Software designed to assist in maintaining and utilizing large collections of data
Entity-Relationship(ER) Model:(Describe objects and their relationships) - Entities: d
- Relationships
- Constraints
create Postgresql:
initdb ~/postgres --create a folder call postgres used to store db data
postgres -D ~/postgres -- start postgres database
ctril+X+C -- terminated the database connection
creatuser -s postgres --create user
kill $(ps aux| grep postgres-- will return a processs id where include postgres) -- kill the service it wi
SQL:
CREATE TABLE Table_name(attr_1_name attr_1_type attr_1_constraint,...)
check (condition): specify an expression which new or updated rows must satisfy for an insert or update operation to succeed
Not Null, Null: the column is not allowed/allowed to contain null values
Deafult: default_expression : Assign a default data value for the column
Unique
Basic Attribute type:
- BooleanType - boolean
- Character Types -char(n)--fixed length, varchar(n)--varying length characters, text --varying length characters without limit
- Numeric Types - integer, serial -- autoincrementing interger, real
- Data'Time Types -timestamp --date+ time, date,time, interval
Define Table:
CRUD Operations:
- Create : Define a new table(Create)
- Integrity Constraint(IC): A condition specified on a database schema and restricts the data that can be stored in the database
- Unique Key: A minimal subset of the columns that uniquely identify a tuple. note: A unique key can be null
- Primary Keys: A minimal subset of the columns that uniquely identify a tuple. note: A primary key shouldn’t be null
- Foreign Keys:
◦ The information stored in a relation linked to the information stored in another relation. If one of the relations is modified, the other must be checked/modified to keep the data consistent. The foreign key in the referencing relation must match the primary key of the referenced relationship. Column names can be different.
◦ Needs to reject or update when referenced information changes.
◦ CASCADE : When a referenced row is deleted/updated, row(s) referencing it should be automatically deleted/updated as well.
◦ NO ACTION (Default) : If any referencing rows still exist when the constraint is checked, an error is raised.
◦ RESTRICT prevents deletion of a referenced row.
◦ SET NULL / SET DEFAULT : When a referenced row is deleted/updated, referencing column becomes Null/a default value.
Foregin Key (id), references custoemr(id), on delete cascade on update cascade
---
### Create/Insert :
Define a new table (CREATE), Insert a tuple (INSERT) into a
table Syntax :
```INSERT INTO table_name(attr_1_name, attr_2_name, ..., attr_n_name)
VALUES (value_1, value_2, ..., value_n), (value_1’, value_2’, ...,
value_n’);
◦ Can omit the list of column names in the INTO clause.
Bulk data loading from a file:
- Syntax:
FROM ‘file_path'
DELIMITER ‘delimieter_character’
[CSV HEADER];
SQL Data type conversion
TO_CHAR(numeric_type, format_string)
9:numeric value
G:group seperater
D: decimal point
S: sign
To_number(text, format_string)
SQL Function
From, where, select, distinct, order by , limit
final exam
- window function
- functions
- CTE
- transactions
- Atomicity(ex: delete, insert statement fail will fail everything, or update everything):
- Actions in transactions are carried out all or non
- Consistency(ex : database will only delete, insert in allowed ways):
- A transcation must change affected data only in allowed ways
- Isolation(because many operation can happen at the same time, isolation allow us to not to worry about when other is doing the transaction )
- Concurrency and isolation( if transaction and select statement happen at the same time, we would isolate the select statement, else, the select statement would output the update data )
- Conflicts and Lock
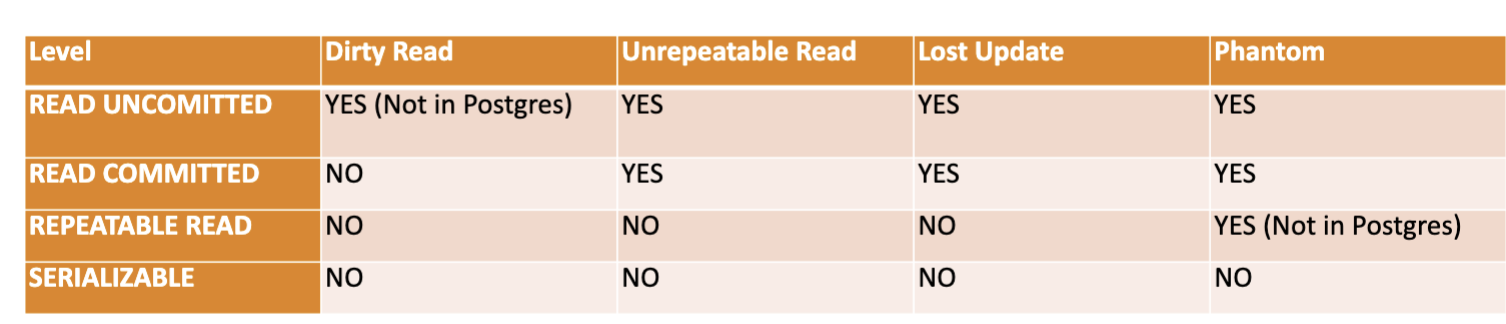
- Durability
- Atomicity(ex: delete, insert statement fail will fail everything, or update everything):
- normal
- ACID
NF:
- issue of un normalized tables: - 1NF(primary key ): - 2NF(unique define) - 3NF(no tranparency )