Microsoft Project
Team 2:
- Molly Behrends
- Payton Bokowy
- Freeman Chen
Institution: Washington State University
Author Note
Do not distribute or use beyond educational purposes.
Table of Contents
Abstract
Understanding partners that are most successful in the Microsoft Partner Network (MPN) is vital for Microsoft. As Microsoft seeks to enter more industries and make their impact larger, they need to know what partners to place more time and resources in and what industries they can expand their reach in. The goal of this report is to uncover the top performing partners, and recommendations for improvements of less successful partners. This paper discusses tasks to be achieved, relevant literature to the research, methods, results, and improvements should further analysis and investigation be done.
The Microsoft Corporation is a front runner in the technology with a revenue of $184.9 billion and specialization on software, hardware, solutions, and services (Johnston, M). These focuses are applied by partners from the Microsoft Partner Network (MPN) which consist of over 400,00 partners worldwide. The partners in the network use Microsoft technologies, and community resources to drive growth for their business. The partnership allows these organizations to improve profitability, develop innovative services and products for its customers, and develop a large advantage over customers. Microsoft invests in these partners by offering advanced selling solutions, technical training and education, and increased mentorship opportunities between Microsoft and their partners. With a large network of partners, it is vital that Microsoft understands who their best partners are and what industries have potential for substantial growth. With a better understanding of partner performance Microsoft will be able to assess beneficial areas to invest their time and resources. This report provides recommendations of partners who Microsoft should place more focus on and recommendations for improved performance for less successful partners.
To address the business problem following objectives and tasks will be used to guide our analysis:
Objectives:
- Identify the top partners from the Microsoft Partner Network
- Find the most successful partners to target potential customers
- Provide recommendations for improved partner success
Tasks:
-
Identify the best partners to bring in the new customers
-
Identify the top partners in each customer industry
-
Identify the best cloud practices for partners to adopt
-
Identify training activities that lead to success.
To help Microsoft identify the top partners, a scoring system was implemented to include the influential attributes. Revenue, active users, consumption, and customer count were used to calculate the ranking of partners. This ranking system helped find the top partners in each industry and the certifications completed for the top partners.
Discovering the top partners in each industry, finding certifications to recommend to partners, and uncovering the best cloud practices to adopt will allow Microsoft to guide their partners toward success. Notable discoveries throughout the project were affects that certification had on partner success, being in multiple industries, growth if only in one workload, and workloads with the most revenue and most used. This report will take a deeper dive in analysis on these findings.
Keywords: Microsoft Partner Network, Top partners, Recommendations
Literature Review
Pareto Distribution
A pareto distribution is also described as the 80-20 rule that accounts for inequalities (Corporate Finance Institute). A pareto distribution is when 20% of partners account for 80% of the revenue. A small portion of partners bring in the most revenue. Business management, company revenue, and employee evaluation can all follow pareto distributions. For this project, the distribution suggests that the focus should be on the small 20% of partners that bring in the majority revenue.
Metascore Magic
The metascore is a weighted average on movies. This scoring system aggregates critics and publications and places a weight on each one. The scores are also normalized. The combined score is the ranking of the movie. The idea of the Metacritic scoring system was used as a basis for the partner scoring system implemented in this project.
Methods
Many analytical methods and data management methods were implemented to uncover top partners, best cloud practices to adopt and certifications that may lead to improved success. Data cleaning and processing were completed before performing any necessary analysis on the dataset.
The data was comprised of 13 tables from Microsoft’s Partner Network which was roughly 100 megabytes in size. The tables consisted of information about Microsoft partners, customers, revenue, consumption, training activities, industries, and performance. Each table contained keys to identify unique partners, customers, industries, certifications, and locations. The keys were changed to a factor type, this allowed for results to be visualized by each partner and remained unique for the duration of the project.
The data consists of partners who are part of three workloads: Azure, Modwrk, or Bizapp. Success for Azure partners are measured by revenue, while success for Modwrk and Bizapp partners are measures by number of active users. Revenue and active usage are primary measures of success, yet they are not the only measures of success. Additional measures of success established for this analysis will be consumption and number of partners. In the exploratory data analysis phase, the distribution of the partner data was skewed and heavy-tailed. This indicates that the partner data follows Pareto Distribution. Pareto Distribution in this instance can be explained as a small percentage of partners who work with a large percent of the customers. This small percentage of partners contributes the most to consumption. Typically, a business would want to spend the most time and resources on the activity or partner who is contributing the most to increase revenue. For the sake of the project analysis, all partners need to be compared equally. Due to the varying measurements of success among workloads, and number of partners with largely different amounts of revenue it would not be fair to compare partners without a scoring system.
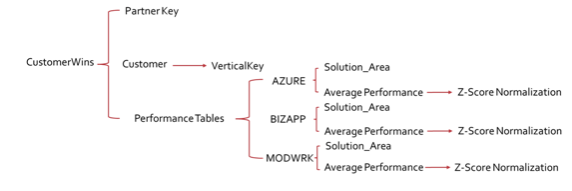
The purpose of the scoring system was to change the values of the success measure columns in the performance tables with a common scale without affecting the other values in the table. A measure matrix is needed so that partners can be placed into an equal scale along with filtering by VerticalKey, SolutionArea and Workloads. The Metacritic movie scoring system was used as a reference for this scoring system because it offers the most balanced aggregate score for each movie from different movie websites like IMDB and Rotten Tomatoes. The Metacritic score is a weighted average that assigns more importance, or weight, to critics and publications more than others based on quality and overall stature (Metacritic). For the nature of this scoring system partners can be thought as of producers, industries as genres, SolutionAreas as ratings and normalized revenue or Active Usage as movie score from the producer in the range of genres and ratings.
Two modifications of the scoring system were implemented before finding the best one. Scoring system 1.0 was focused on the SolutionArea average performance for each partner and filtered on the specific VerticalKey. The first scoring system was not sufficient because each partner could perform differently in the same SolutionArea based on the VerticalKey they are working in. To combat this, Scoring System 2.0, as seen in Figure 3, is grouped by PartnerKey and VerticalKey which allowed the partner average performance to be used in the SolutionArea based on VerticalKey.
The scoring system scaled the revenue for Azure and Active Users for Modwrk and Bizapp; this scaled the values from –3 to 3. The columns were merged to create one column of success. Then, the columns for consumption and number of customers were also scaled. These were summed up to get one metric for each partner. From this, the highest valued partner is ranked the most successful. The scoring system is used throughout the analysis of finding the top partners in each industry and finding what certifications the top partners use.
Using the results from the scoring system, the top partners were easily found. To find the top partners in each industry the partners were matched with their industry. Uncovering the most useful certifications also utilized the scoring system. A pivot table was created to illustrate all the partners and how many employees they had complete all the different certifications. The number of people taking each certification was summed up; if no one had taken the certification, the column was removed. This table was then matched with the most successful partners from the scoring system. It looked at the top 10 partners certifications. From there, the certifications that were commonly taken were recommended for the other partners to require their employees to take those certifications.
To find the next best cloud practice for a partner in a particular industry, an advanced SQL subquery was utilized. A left outer join was implemented to connect the three performance tables of interest (PerformanceAzure, PerformanceBizapp, PerformanceModwrk) with the Customer table. This way, a specific industry can match with each task and their respective cloud service used. After joining the tables, the number of times a cloud service is used was counted, which will tell the most demanded service, as well as the recommendation. the recommendation was based off the second most demanded service for each industry. To rank the cloud services based off demand, nested case statements were employed. In the case statements, the first condition was to grab the most used service, and then the nested condition, the second most used service was grabbed.
To get the most and second most used cloud practice, two SQL case statements were written. Although it may seem redundant, this was the best possible solution when using case statements, and the time to run the code wasn’t too detrimental (about ~15 seconds longer). When running the query, the outputs received are the industry keys, the number of times a cloud service is used (countBizapp, countAzure, countModwrk), the most used product, and the recommendation.
Results
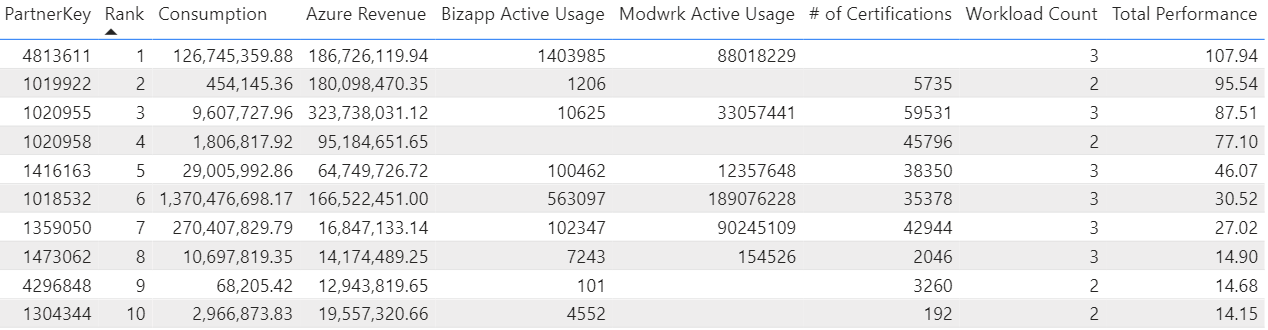
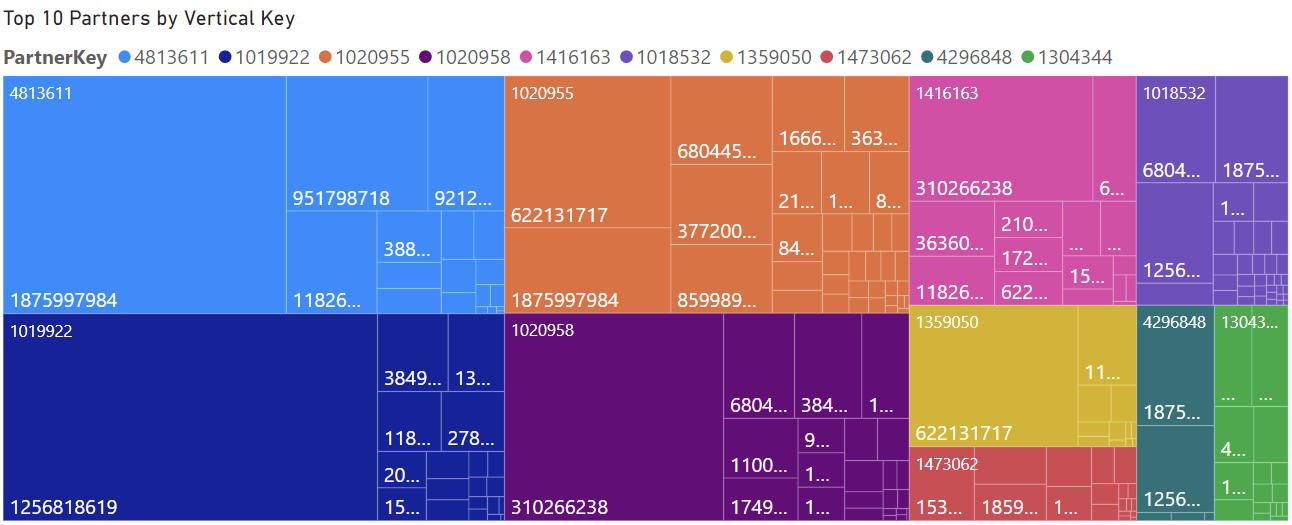
After implementing the scoring system, the top partners were ranked accordingly. A tree map was created with PowerBI to illustrate the top partner and the industries each partner is in. The tree map can be seen in Figure 1. The table in Table 1 also correlates to the top partners. The table outputs the data for each top partner. Both the tree map and the table reinforce the finding that the top partner was Partner 4813611. Partner 4813611 had a consumption of 126,745,359.98, Azure revenue of 186,726,119.94, Bizapp Active Usage of 1,403,985, Modwrk Active Usage of 88,018,229, activity in all 3 workloads, but no certifications. All top 10 partners shown in the table had over 3,000 certifications and most of them were in two if not all three workloads. Another feature the tree map illustrates is that the top 10 partners are in many industries. These insights will help encourage partners who are less successful to expand to more industries or additional workloads.
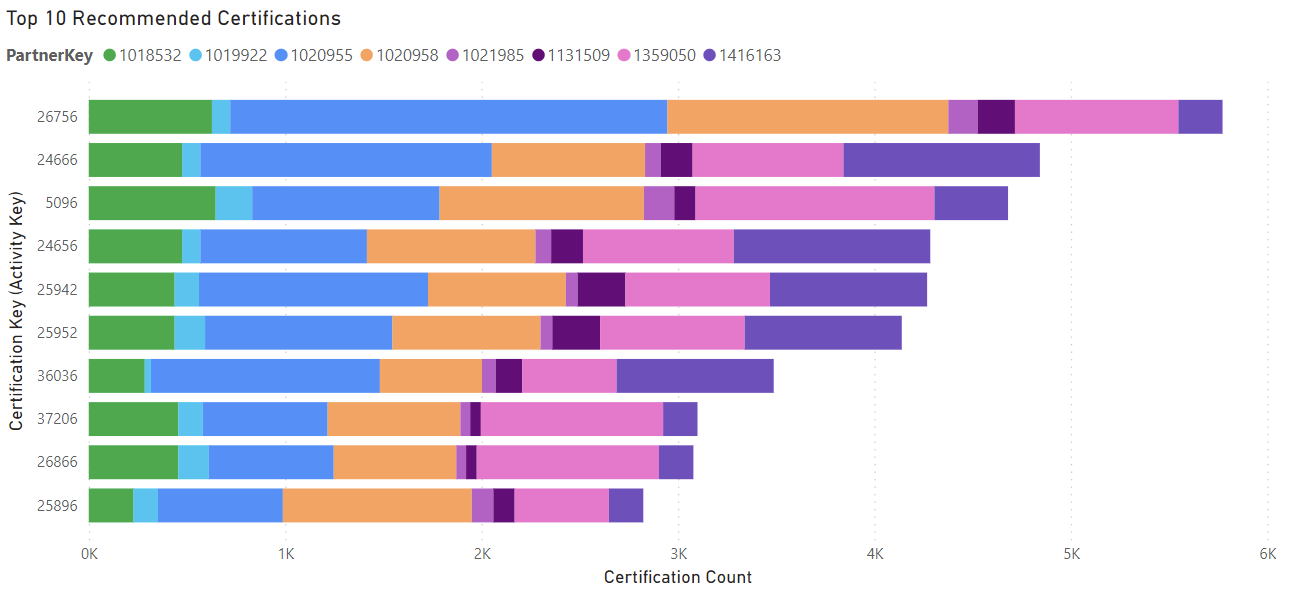
To visualize the recommended training activities, a stacked bar chart was used. Figure 2 demonstrates the top 10 certifications recommended to all Microsoft partners. Only 8 partner keys are shown in the stacked bar chart because 2 of the top 10 partners had no certifications. Partner 1020955 had the most certifications out of the top 10 partners. The certification with the highest number of partners certified was ActivityKey 26756 with over 6,000 certifications. This is the most used certification from the top 10 partners. The chart illustrating the training activities that lead to success will assist the less successful partners in becoming more successful.
When recommending the next cloud practice a partner should adopt, the user should take the decomposition tree map into account. The decomposition tree map in Figure 4 illustrates the best next cloud practice for partners in a specific industry. There are 83 different industries, and Modwrk is the most used product in 78 of the 83 industries. Of those industries, Bizapp is recommended for 66 of those industries. The decomposition tree illustrates all the vertical keys for each recommended cloud practice. Most partners are recommended to adopt Bizapp. Figure 4 illustrates that Bizapp is the recommended practice for vertical keys 229499, 36360725, and 64 other vertical keys.
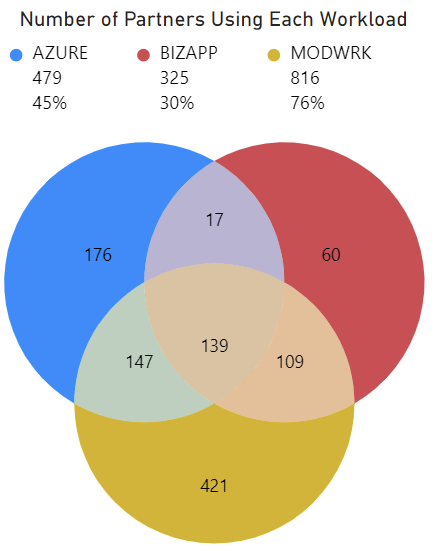
To reiterate, most of the top 10 partners are in 3 workloads, being in multiple workloads leads to more success. The Venn diagram in Figure 5 shows the number of partners that are using each workload. This visual can be used to recommend other workloads that partners can expand to. Exactly 139 partners use all three workloads, 176 partners use only Azure, 60 partners use only Bizapp, and 421 partners use only Modwrk. These insights will help Microsoft determine what workloads is best for partners to expand into.
Improvements
After our analysis, a few improvements discussed was to improve the scoring system, and analyze disproportionality in a particular workload. Adding weights that are based on consumption and the status of the SolutionKey would help improve the scoring system. This would ultimately influence the scoring process by deciding how much the scores from SolutionKey and VerticalKey would affect the output. This would make the partners more balanced. A second improvement would be to analyze disproportionate revenues in a specific revenue using out Venn diagram or box and whisker plots instead. Using the Venn diagram, further analyze on a specific VerticalKey would give insights if one VerticalKey drives a Workload more than another. This would help the business development team see patterns with the best performing Workload. A box and whisker plot could be used instead of the Venn diagram so that each VerticalKey could be shown at once. Both these improvements could better our analysis and recommendations for Microsoft and their partners.
Conclusion
The main objective of the project was to identify Microsoft’s top partners, so they can focus their efforts on those top performing partners. Finding the top partners in each industry helped achieve this objective. After finding the top partners, it is important to find areas where less successful partners can improve. Expanding to more than one workload and taking more certifications that the top partners take are the two biggest actions a partner can take to become more successful. Finding the next best cloud practice to adopt and certifications to recommend will improve those partners. The next best cloud practice will tell the partner what other workload they should adopt. The certifications used by the top partners in their industry should be the certifications the partner should recommend their employees to take. To help Microsoft find the top partners, a scoring system to rank partners was created. The scoring system took information about each partners’ revenue, consumption, active usage, customer counts, and certification counts to best rank the partners. Visualizations and filters from Power BI helped visualize the findings of this project.
References
Corporate Finance Institute. Pareto Distribution. https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/economics/pareto-distribution/
Johnston, M. (2022, March 04). Biggest Companies in the World by Market Cap. Investopedia. https://www.investopedia.com/biggest-companies-in-the-world-by-market-cap-5212784
Metacritic. How We Create the Metascore Magic. https://www.metacritic.com/about-metascores#:~:text=We%20carefully%20curate%20a%20large,critical%20opinion%20in%20one%20Metascore.
Tables
- Top 10 Overall Microsoft Partners
Figures
- Top 10 Overall Microsoft Partners
- Top 10 Recommended Certifications
- Adaptive Scoring System 2.0 Model
- Best Next Cloud Practice Chart

- Workload Usage by Partners